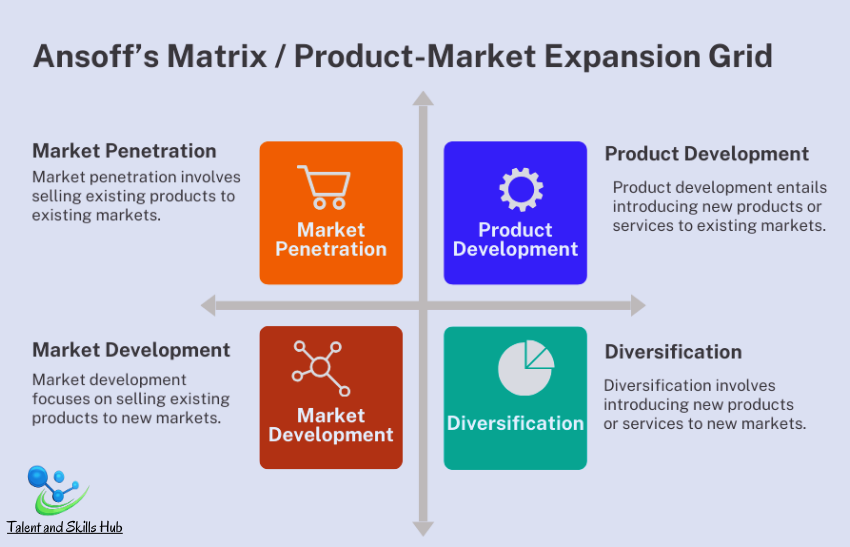
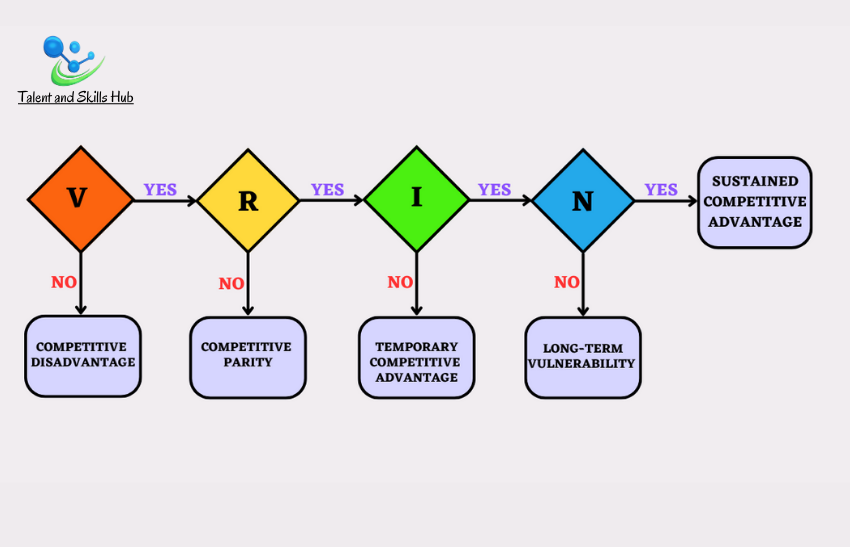
Ansoff’s Matrix, also known as the Product-Market Expansion Grid, is a strategic framework that helps businesses and marketers to analyse and plan their growth strategies. The model was developed by Igor Ansoff, a Russian-American mathematician and business manager. The matrix provides four growth strategies based on two dimensions: products and markets. The matrix consists of four quadrants, each representing a different growth strategy:
1. Market Penetration:
Market penetration involves selling existing products to existing markets. The goal is to increase market share, customer base, or sales within the current market.
Examples: Offering promotions, increasing advertising, or improving product features to attract existing customers or gain new ones in the same market.
2. Market Development:
Market development focuses on selling existing products to new markets. This strategy involves entering new geographic areas, demographic segments, or distribution channels.
Examples: Expanding to international markets, targeting new customer segments, or establishing partnerships to reach untapped markets.
3. Product Development:
Product development entails introducing new products or services to existing markets. This strategy aims to leverage existing customer relationships and market knowledge.
Examples: Introducing new product variations, improving existing products, or launching complementary products to meet the evolving needs of current customers.
4. Diversification:
Diversification involves introducing new products or services to new markets. This is the most risk-oriented strategy, as it requires entering unfamiliar territories both in terms of products and markets.
Examples: Entering completely new industries, acquiring companies with different product lines, or pursuing unrelated business ventures.
There are two types of diversification a firm can employ:
- Related diversification: With this type of diversification, a firm can leverage on the synergies of the existing product/market to succeed in the new product/market. For example, a leather shoe producer that starts a line of leather wallets or accessories is pursuing a related diversification strategy.
- Unrelated diversification: There are no potential synergies to be realized between the existing business and the new product/market in this type of diversification. For example, a leather shoe producer that starts manufacturing phones is pursuing an unrelated diversification strategy.
WATCH THE VIDEO HERE>>>
How to Use Ansoff’s Matrix and Product Market Grid
Using Ansoff’s Matrix, or the Product-Market Expansion Grid, involves assessing your current business situation and determining the most suitable growth strategy you want to employ. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use Ansoff’s Matrix:1.
1. Understand Your Current Position:
- Analyse your existing products and services.
- Evaluate your current target markets and customer segments.
- Assess your market share and competitive position.
2. Identify Growth Objectives:
- Clearly define your growth objectives, whether it’s increasing sales, expanding market share, entering new markets, or launching new products.
3. Consider Market Penetration:
- If your goal is to increase sales within your existing market:
- Focus on marketing and promotional activities.
- Explore opportunities to enhance product features or quality.
- Consider loyalty programs to retain existing customers.
4. Explore Market Development:
- If you aim to enter new markets or reach new customer segments:
- Conduct market research to identify potential markets.
- Adapt your products or services to meet the needs of different demographics.
- Develop distribution channels to reach new geographic areas.
5. Evaluate Product Development:
- If the goal is to introduce new products to existing markets:
- Innovate and create new product variations.
- Enhance existing products based on customer feedback.
- Consider partnerships or collaborations for product improvements.
6. Assess Diversification:
- If you’re looking to diversify into new products and new markets:
- Conduct a thorough risk assessment.
- Consider the feasibility and compatibility of entering new industries.
- Plan for additional resources and capabilities required for diversification.
7. Balance Risk and Reward:
- Consider the risk and reward associated with each growth strategy.
- Evaluate your organization’s capacity for change, financial resources, and expertise in implementing each strategy.
8. Develop Action Plans:
- Once you have identified the most suitable growth strategy, develop detailed action plans.
- Outline the steps, timelines, and resources required for implementation.
- Also establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the success of your growth initiatives.
9. Monitor and Adjust:
- Regularly monitor the progress of your growth strategies.
- Collect feedback and data to assess the effectiveness of your initiatives.
- Be prepared to adjust your strategies based on market changes and evolving business conditions.

How to Assess the Risk of Each Strategy
Assessing the risk of each strategy in Ansoff’s Matrix involves a careful examination of various factors that could impact the success or failure of the chosen growth path. Here are key considerations for assessing the risk associated with each strategy:
1. Market Penetration:
- Competition Intensity: Evaluate the level of competition in the existing market. High competition may pose challenges for gaining additional market share.
- Market Saturation: Consider whether the market is already saturated, making it difficult to achieve significant growth without new strategies.
2. Market Development:
- Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Assess the cultural and regulatory differences in new markets. These variations can pose challenges in terms of product acceptance and compliance with local laws.
- Market Research: Conduct thorough market research to understand the needs and preferences of the new target audience.
3. Product Development:
- Innovation Risks: Evaluate the risks associated with innovation and product development. There may be uncertainties regarding the market acceptance of new products.
- Development Costs: Consider the financial investment required for research, development, and marketing of new products.
4. Diversification:
- Industry Knowledge: Assess your organization’s knowledge of the new industry. Lack of understanding may lead to strategic missteps.
- Resource Allocation: Diversification often requires significant resources. Evaluate whether your organization has the financial and human resources for this expansion.
Further Considerations:
- Economic Factors: Consider economic conditions that could impact consumer spending, production costs, and overall market conditions.
- Technological Changes: Evaluate how technological advancements may affect your industry and chosen strategies.
- Political and Regulatory Environment: Assess potential risks associated with changes in government policies, trade regulations, or other political factors.
SWOT Analysis:
Conduct a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) for each strategy to identify internal and external factors influencing the success or failure of the chosen approach.
Scenario Planning:
Develop scenarios for potential future events that could impact the success of the chosen strategy. This helps in preparing for different outcomes.
Risk Mitigation Strategies:
Identify and plan for risk mitigation strategies. This may involve developing contingency plans, diversifying risk, or establishing partnerships to share potential burdens.
Monitoring and Adaptation:
Establish a system for continuous monitoring of key performance indicators and market conditions. Be prepared to adapt strategies based on real-time feedback and changing circumstances.
Final Remark
The Product-Market Expansion Grid is a versatile tool that allows businesses to consider different growth options and tailor their strategies based on their specific goals, resources, and risk tolerance. It provides a structured approach to decision-making in the context of business expansion and development.
By systematically applying Ansoff’s Matrix, businesses can make informed decisions about their growth strategies, aligning them with their overall business objectives and market conditions. This structured approach can help to minimise risks and maximise the chances of successful growth.
It’s important to note that risk assessment is an ongoing process. Organizations should regularly review and update their risk assessments as market conditions, industry dynamics, and internal capabilities evolve over time.
Reference.
Ansoff, I. H. (1965). Corporate Strategy: An Analytic Approach to Business Policy for Growth and Expansion. McGraw-Hill.