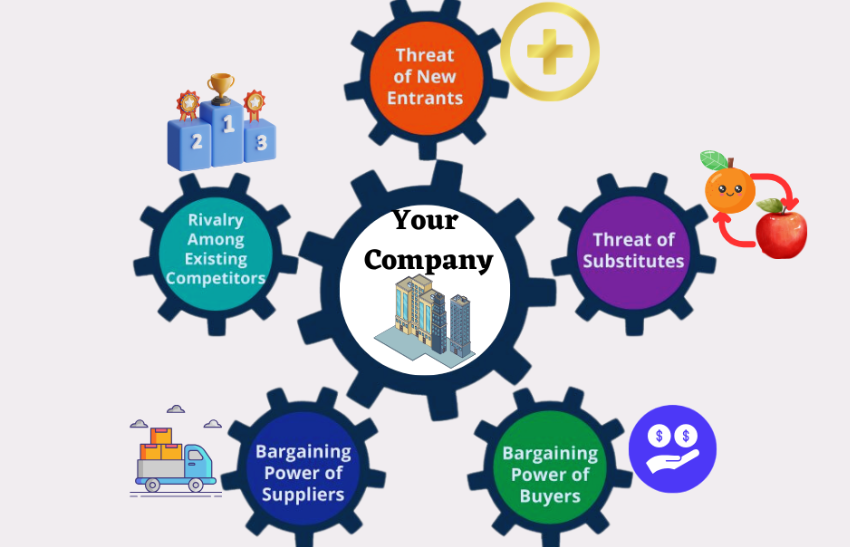
The Five Forces Analysis, developed by Michael Porter, is a framework for assessing the competitive forces within an industry that shape and influence the intensity of competition. This analysis helps businesses understand the attractiveness of an industry, identify potential sources of competition, and formulate strategies to position themselves effectively. The five forces are:
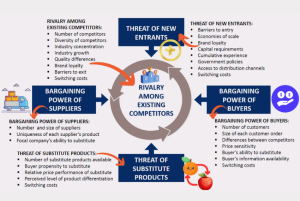
- Threat of New Entrants:
This force assesses the ease with which new companies can enter a particular industry and compete with existing players. Factors that increase the threat of new entrants include low barriers to entry, low capital requirements, and low brand loyalty. However, high entry barriers, such as strong brand identity, economies of scale, and government regulations, can reduce the threat and discourage new entrants into the industry.
- Bargaining Power of Buyers:
The bargaining power of buyers examines the influence that customers have over the industry. If buyers have high bargaining power, they can demand lower prices, higher quality, or better services. Factors such as the availability of alternative products, the standardization of products, and the concentration of buyers relative to sellers influence buyer power. Strong buyer power is a threat to industry profitability.
Some of the strategies to reduce the bargaining power of buyers include product differentiation, building brand loyalty, creating switching costs, offering value-added services, maintain control over the supply chain to ensure that there are limited alternative sources available to buyers. Build strong relationships with your customers based on trust and mutual benefit. Continuously innovate and improve your products or services to stay ahead of competitors. Use legally binding contracts and agreements to set terms and conditions that limit buyers’ ability to negotiate extensively.
- Bargaining Power of Suppliers:
This force assesses the influence that suppliers have over the industry. If suppliers have high bargaining power, they can demand higher prices for inputs, affecting the profitability of companies within the industry. Factors such as the uniqueness of inputs, the availability of substitute inputs, and the concentration of suppliers relative to buyers impact supplier power.
Some of the strategies to reduce the bargaining power of suppliers include working with multiple suppliers for the same or similar goods or services. Consider vertical integration by acquiring or establishing your own sources of supply. Build strong relationships with your suppliers based on mutual trust and collaboration. This can lead to more favourable terms and conditions in negotiations. Negotiate long-term contracts with suppliers to secure stable pricing and ensure a steady supply of goods or services. This reduces the risk of price fluctuations and strengthens your bargaining position. Invest in research and development to develop alternative technologies or processes that reduce reliance on specific inputs or suppliers. Implement cost leadership strategies to drive down costs throughout the supply chain. This can give you leverage in negotiations by making it difficult for suppliers to raise prices without losing your business. Stay informed about market trends, including changes in supply and demand dynamics, pricing, and supplier behaviour. This knowledge allows you to anticipate and respond to supplier tactics effectively.
- Threat of Substitute Products or Services:
This force considers the availability of alternative products or services that could replace those offered by companies in the industry. The higher the availability of substitutes, the more intense the competition. Factors influencing the threat of substitutes include price, performance, and ease of switching. Industries with few or no substitutes generally have more pricing power.
Reducing the threat of substitutes involves making your product or service unique or indispensable to customers, thereby minimizing the likelihood that they will switch to alternatives. Here are some strategies to consider: Differentiate your product or service from substitutes by offering unique features, benefits, or experiences that address specific customer needs or preferences. Invest in building strong brand loyalty among customers through marketing, customer service, and product quality. A loyal customer base is less likely to switch to substitutes even if they are available, as they perceive greater value in your brand. Continuously innovate and improve your product or service to stay ahead of potential substitutes. This could involve introducing new features, technologies, or functionalities that make your offering more desirable and difficult to replicate. Form exclusive partnerships or collaborations with suppliers, distributors, or other stakeholders to create barriers to entry for potential substitutes.
Maintain competitive pricing relative to substitutes to retain customers. Educate customers about the unique benefits and value proposition of your product or service compared to substitutes. Highlighting the advantages of choosing your offering can help customers make informed decisions and reduce the likelihood of switching to substitutes. Build strong relationships with customers through personalized interactions, excellent customer service, and ongoing engagement. Establishing a connection with customers can foster loyalty and reduce the likelihood of them seeking substitutes. Explore opportunities to expand into new markets or segments where the threat of substitutes is lower. Diversifying your customer base can help mitigate the impact of substitutes in existing markets.
- Intensity of Competitive Rivalry:
This force evaluates the degree of competition among existing firms in the industry. Factors contributing to high rivalry include a large number of competitors, slow industry growth, high fixed costs, and lack of differentiation. Intense competition can lead to price wars, reduced profitability, and increased innovation as companies vie for market share.
Reducing the intensity of competitive rivalry involves strategies aimed at creating a less hostile and more sustainable competitive environment. Here are several approaches you can consider: Develop unique features, designs, or functionalities that distinguish your products or services from competitors. This differentiation can reduce direct competition and mitigate price wars. Concentrate your efforts on serving specific niche markets where competition is less intense. By catering to specialized customer needs, you can establish a stronger market position with fewer direct competitors. Invest in building strong brand loyalty among customers through consistent branding, quality products, and exceptional customer service. Loyal customers are less likely to switch to competitors solely based on price, reducing competitive pressure.
Form strategic alliances or partnerships with other companies to pool resources, share expertise, and collectively compete against rivals. Collaboration can help reduce rivalry by increasing market power and expanding market reach. Prioritize delivering exceptional customer experiences at every touchpoint. By exceeding customer expectations, you can build customer loyalty and reduce the significance of price competition. Implement cost leadership strategies to achieve economies of scale and cost efficiencies that allow you to offer competitive prices while maintaining profitability.
Invest in research and development to continuously innovate and improve your products or services. Innovation can create barriers to entry for competitors and differentiate your offerings in the market. Segment the market and tailor your marketing and product offerings to specific customer segments. By focusing on distinct market segments, you can reduce direct competition and increase customer loyalty. Keep a close eye on competitors’ actions, including pricing strategies, product launches, and marketing campaigns. Respond strategically to competitive moves to maintain your competitive advantage.
WATCH THE VIDEO HERE>>>
How to Use Five Forces Analysis:
- Identify Key Factors:
Identify and evaluate the key factors that influence each of the five forces within your industry.
- Assess the Strength of Each Force:
Determine the strength of each force and its impact on industry structure. Consider whether each force is high, medium, or low.
- Understand Industry Attractiveness:
Assess the overall attractiveness of the industry based on the combined influence of the five forces. An attractive industry is one where the forces are relatively weak.
- Formulate Competitive Strategies:
Develop strategies to respond to the identified forces. For example, companies may focus on differentiation, cost leadership, or innovation to mitigate the impact of highly competitive rivalry.
Final Remark
Five Forces Analysis is a valuable tool for strategic planning, helping businesses identify areas of opportunity and threats within their industry. It provides a systematic way to analyse the competitive forces and formulate strategies that can enhance a company’s competitive position.
References
Porter, M. E. (1980). “Competitive Strategy: Techniques for Analysing Industries and Competitors.” Free Press.
Porter, M. E. (2008). “The Five Competitive Forces That Shape Strategy.” Harvard Business Review.