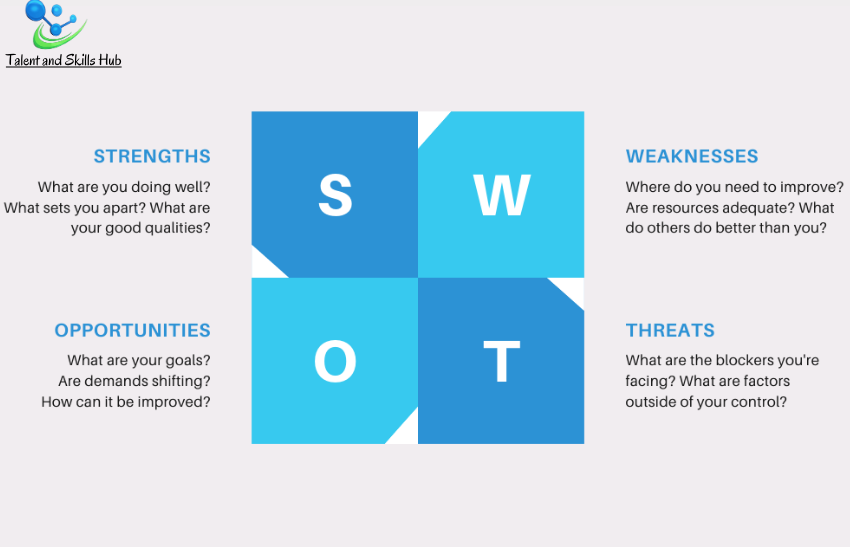
SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used by organizations to identify and assess internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities, and threats. The acronym “SWOT” stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. This analysis helps organizations understand their current position and make informed decisions about future strategies. Here’s an overview of each component:
-
Strengths (Internal):
Internal factors that give an organization a competitive advantage or contribute to its success.
Examples: Strong brand reputation, skilled workforce, innovative products or services, efficient processes, financial stability.
-
Weaknesses (Internal):
Internal factors that put the organization at a disadvantage or hinder its success.
Examples: Limited resources, outdated technology, weak management, poor employee morale, inefficient processes.
-
Opportunities (External):
External factors in the environment that can be leveraged to the organization’s advantage.
Examples: Emerging market trends, technological advancements, changes in consumer behaviour, new partnerships or collaborations, regulatory changes.
-
Threats (External):
External factors that could pose challenges or risks to the organization.
Examples: Intense competition, economic downturns, changes in regulations, technological disruptions, geopolitical uncertainties.
WATCH THE VIDEO HERE>>>
Significance of SWOT Analysis
- Strategic Planning: SWOT analysis helps organizations formulate strategies by providing a comprehensive understanding of internal and external factors that may impact their objectives.
- Identification of Strengths and Weaknesses: By examining internal factors, such as resources, capabilities, and competencies, SWOT analysis highlights areas where the organization excels (Strengths) and areas needing improvement (Weaknesses).
- Assessment of Opportunities and Threats: SWOT analysis evaluates external factors like market trends, competitor actions, regulatory changes, and economic conditions to identify potential opportunities for growth and areas of threat or risk.
- Decision Making: It assists in decision-making processes by providing insights into the potential outcomes and risks associated with different courses of action.
- Competitive Advantage: SWOT analysis helps organizations leverage their strengths to exploit opportunities and mitigate threats, thereby gaining a competitive advantage in the market.
- Resource Allocation: It aids in prioritizing resource allocation by focusing on areas where the organization has strengths and opportunities while addressing weaknesses and threats.
- Enhanced Communication: SWOT analysis facilitates communication and collaboration among stakeholders by providing a structured framework for discussing internal and external factors affecting the organization.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly conducting SWOT analysis allows organizations to adapt to changing internal and external environments, fostering continuous improvement and innovation.
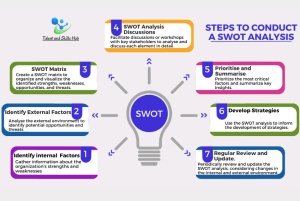
Steps to Conduct a SWOT Analysis:
- Identify Internal Factors:
Gather information about the organization’s strengths and weaknesses through internal assessments, employee feedback, and performance evaluations.
- Identify External Factors:
Analyse the external environment to identify potential opportunities and threats. This involves examining market trends, industry dynamics, and the competitive landscape.
- SWOT Matrix:
Create a SWOT matrix to organize and visualize the identified strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
- SWOT Analysis Discussions:
Facilitate discussions or workshops with key stakeholders to analyse and discuss each element in detail. Explore the relationships between internal and external factors.
- Prioritize and Summarize:
Prioritize the most critical factors and summarize key insights. Focus on those elements that have the greatest impact on the organization’s strategic decisions.
- Develop Strategies:
Use the SWOT analysis to inform the development of strategies. Capitalize on strengths, address weaknesses, seize opportunities, and mitigate threats.
- Regular Review and Update:
Periodically review and update the SWOT analysis, considering changes in the internal and external environment. This ensures that the organization remains agile and responsive to evolving conditions.
Final Remark.
SWOT analysis is a versatile tool applicable to various levels of decision-making, from individual projects to overall strategic planning for an organization. It provides a comprehensive view of the internal and external factors that influence success and helps organizations align their strategies with their unique circumstances.