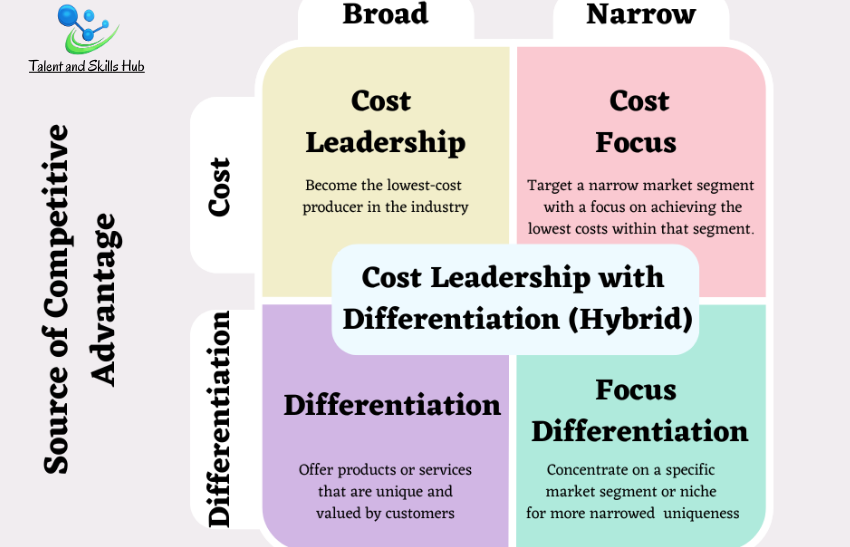
Porter’s Generic Strategies is a strategic management framework developed by Michael Porter. It outlines four primary strategies that businesses can adopt to gain a competitive advantage and achieve superior performance in their industry. The four generic strategies are cost leadership, cost focus, differentiation, and focus differentiation. Here’s an overview of each:
1. Cost Leadership:
Objective: Become the lowest-cost producer in the industry.
Key Characteristics:
- Efficient production processes to achieve economies of scale.
- Tight cost control and cost minimization throughout the value chain.
- Price competitiveness to attract a broad market.
Target: Aims at a broad market, appealing to cost-sensitive customers.
Example 1: Walmart.
Walmart is known for its cost leadership strategy. The company focuses on operational efficiency, supply chain management, and economies of scale to offer low prices to a broad customer base.
Example 2: Southwest Airlines.
Southwest Airlines follows a cost leadership strategy in the airline industry. By utilising a single type of aircraft, efficient turnaround times, and point-to-point routes, Southwest can maintain lower operational costs and provide affordable air travel.
2. Cost Focus:
Objective: Target a narrow segment of the market but with a focus on achieving the lowest costs within that segment.
Key Characteristics:
- Targets a specific niche market.
- Emphasizes cost minimization within the niche.
- Offers competitive pricing.
- May still differentiate products/services.
- Requires deep understanding of customer needs.
- Demands flexibility and adaptability.
- Involves careful risk management.
Target: Minimizing costs and offering competitive prices to a specialised group of customers to gain a competitive edge in the industry.
Example 1: Dollar General.
Dollar General operates discount retail stores primarily in rural and suburban areas, targeting price-conscious consumers. By focusing on cost efficiency in areas such as store layout, inventory management, and supply chain operations, Dollar General offers a wide range of low-priced merchandise to its customers.
Example 2: Aldi Supermarket.
Aldi is a global discount supermarket chain known for its no-frills approach to retailing. By streamlining operations, offering a limited selection of private-label products, and maintaining a lean staffing model, Aldi is able to keep costs low and pass on savings to customers, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious shoppers.
3. Differentiation:
Objective: Offer products or services that are unique and valued by customers.
Key Characteristics:
- Emphasis on innovation, quality, brand image, and marketing.
- Product features and attributes that distinguish the offering from competitors.
- Focus on premium pricing to cover the costs of differentiation.
Target: Targets a broad market or specific segments willing to pay a premium for unique features.
Example 1: Apple
Apple differentiates itself through innovative product design, premium quality, and a strong brand image. The unique features of Apple products, along with a focus on user experience, set the company apart in the consumer electronics market.
Example 2: Nike
Nike employs a differentiation strategy in the athletic footwear and apparel industry. The company invests heavily in product innovation, endorsements with high-profile athletes, and marketing campaigns that emphasize style and performance.
4. Focus Differentiation:
Objective: Concentrate on a specific market segment or niche.
Key Characteristics:
- Tailoring products or services to meet the needs of a particular segment.
- Developing expertise and competitive advantage in a narrow market scope.
- Flexibility to adapt to the specific demands of the chosen segment.
Target: Targets a narrow market segment or niche where the company can excel.
Example 1: Rolex
Rolex adopts a focus strategy by targeting a narrow market segment of luxury watch buyers. The brand’s emphasis on craftsmanship, precision, and exclusivity appeals to consumers seeking high-end timepieces.
Example 2: Dollar Shave Club
Dollar Shave Club focuses on a niche market within the personal care industry—affordable and convenient razor subscriptions. By catering to a specific segment, the company has gained a competitive edge.
WATCH THE VIDEO HERE>>>
Combination Strategies:
Companies can also pursue a combination of these strategies:
Cost Leadership with Differentiation (Hybrid): Offering reasonably priced products with some unique features.
Cost Focus: Concentrating on cost leadership within a specific market segment.
Differentiation Focus: Offering unique products or services within a narrow market segment.
Example 1: Toyota
Toyota combines elements of cost leadership and differentiation. While offering reliable and cost-effective vehicles, the company also emphasizes innovation, quality, and a diverse product line to appeal to a broad customer base.
Example 2: Amazon
Amazon is known for its hybrid strategy. It started as an online bookstore with a focus on cost leadership. Over time, it expanded its offerings, invested in technological innovation, and differentiated itself through services like Amazon Prime.
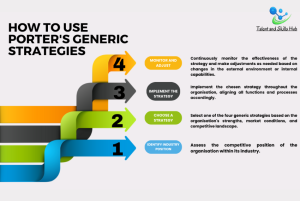
How to Use Porter’s Generic Strategies:
- Identify Industry Position:
Assess the competitive position of the organisation within its industry.
- Choose a Strategy:
Select one of the four generic strategies based on the organisation’s strengths, market conditions, and competitive landscape.
- Implement the Strategy:
Implement the chosen strategy throughout the organisation, aligning all functions and processes accordingly.
- Monitor and Adjust:
Continuously monitor the effectiveness of the strategy and make adjustments as needed based on changes in the external environment or internal capabilities.
Final Remark.
Porter’s Generic Strategies provide a framework for businesses to make strategic choices that align with their competitive advantage. The goal is to achieve sustainable differentiation or cost leadership and effectively compete in the market.